|
Characterizations and applications of nanomaterials |
|||||
High-efficiency photo-electron conversion devices Semiconductor processes and nanofabrication Characterizations and applications of nanomaterials Optical characterization of graphene Graphene-gold oxide photodetector Optical analysis of hollow gold nanoparticles Photomodification of hollow gold nanoparticles for high-density data storage Light harvesting and light extraction Light extraction efficiency of LEDs Antireflection structures for solar cells Optical analysis techniques Eco-friendly devices and sensors
|
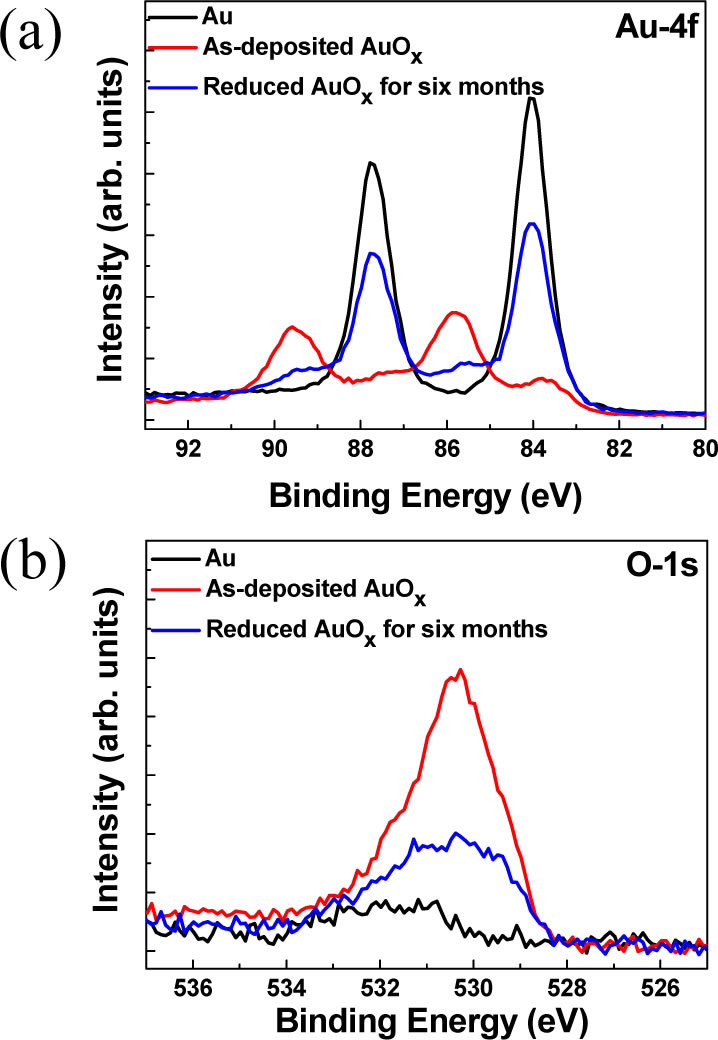
Controllable Localized Surface Plasmonic Resonance Phenomena in Reduced Gold Oxide Films In this study, we used reactive sputtering to prepare large-area, homogeneous gold oxide (AuOx) films, which we then subjected to reduction processes under ambient conditions at room temperature to obtain reduced AuOx films featuring embedded Au nanoparticles (NPs). We analyzed these films in terms of both their material characteristics and optical properties. For the first time, we obtained the optical constants of AuOx films directly deposited on glass and Si substrates. Moreover, we observed localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) phenomena from the visible to the near-infrared (NIR) during the formation of the Au NPs in the AuOx film. The plasmonic properties of the Au NPs embedded in the AuOx films were much different from those of chemically synthesized Au NPs. We found that the LSPR wavelength of the Au NPs embedded in the AuOx films could be tuned from 700 to 980 nm by varying the duration of the reduction process. Moreover, the reduced AuOx films could be applied as surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS)-active substrates. The minimum detection was achieved down to a concentration of 10−10 M (R6G) when using the reduced AuOx film-based substrate−a level comparable with those of other kinds of SERS substrates prepared using more complicated methods. The rapid method proposed herein provides large-areas films with tunable resonance wavelengths for applications as SERS-active substrates in optical and chemical sensing. |
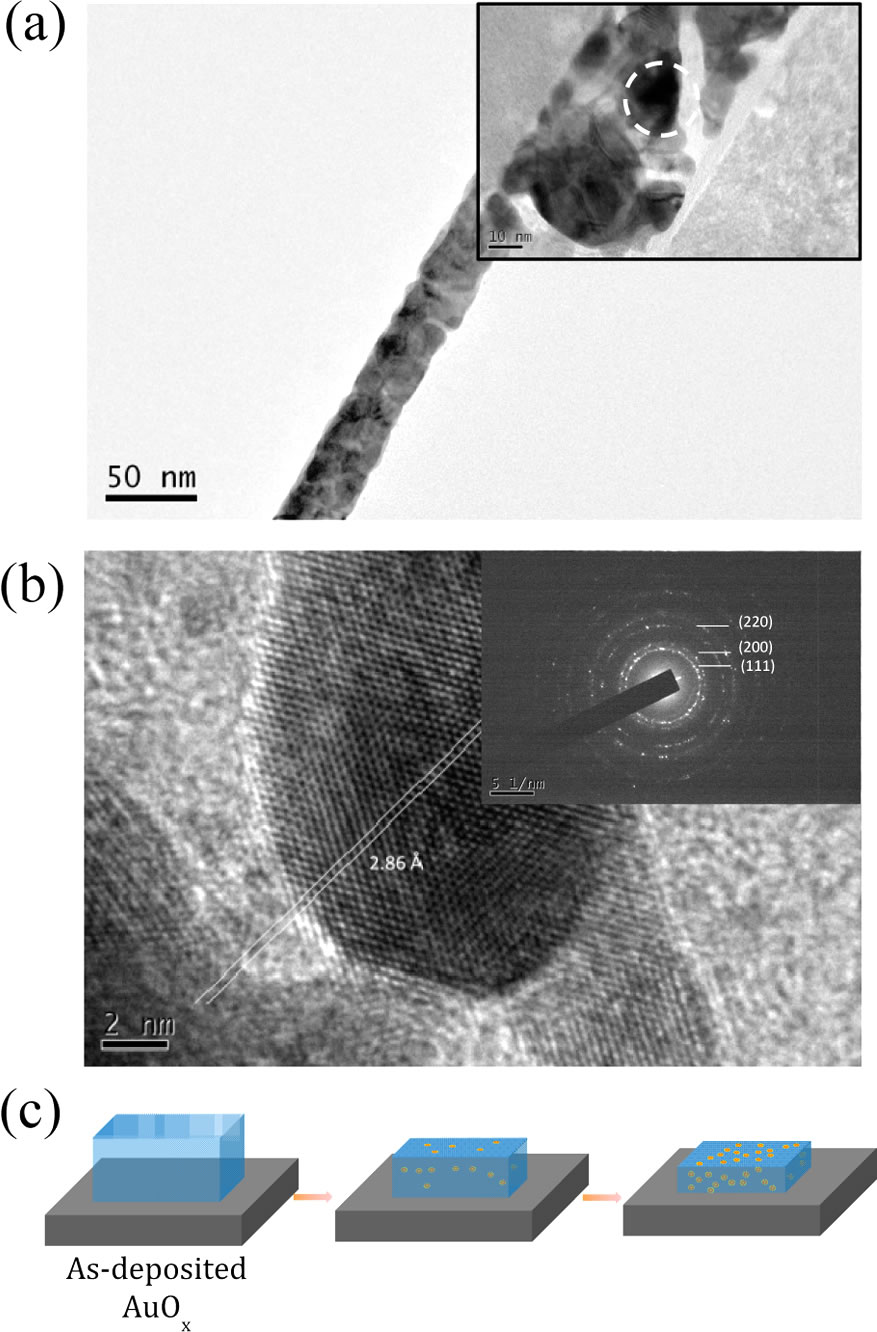
(a) TEM image of a AuOx film that had been reduced under ambient conditions for six months; inset: enlarged image. (b) HRTEM image and SAED pattern of the reduced AuOx film; the analysis region is indicated by the white circle in the inset to (a). (c) Schematic representation of the formation of Au NPs on the surface of a AuOx film during the reduction process.
|
|||
Copyright(c) 2008 Nano-optpelectronics Lab., Department of Material Science and Engineering, National Taiwan University No. 1, Sec. 4, Roosevelt Road, Taipei, 10617 Taiwan(R.O.C) Phone:+886-2-3366-3240 Fax:+886-2-2362-7651 |
|||||